
Welcome back to LNG4U — your gateway to the stories shaping the LNG landscape.
We start with a sharp insight to give you that edge 🎓, then dive straight into the big moves stirring the market — from prices 💰 to offshore game-changers 🚢. Quick reads. Real signals. Let’s get into it.
🎓 LNGKnowledge
A liquified gas 💧 is the liquid form of a substance which, at ambient temperature and at atmospheric pressure, would be a gas 💭.
The most important of a liquefied gas 💧, in relation to pumping and storage, is its saturated vapour pressure 📈. This is the absolute pressure exerted when the liquid is in equilibrium with its own vapour at a given temperature.
The Gas Carrier Codes relates saturated vapour pressure to temperature 🌕 and has adopted the following definition the liquified gases carried by sea :
👉 Liquids with a vapour pressure exceeding 2.8 bar absolute at a temperature of 37.8°C".
An alternative way of describing a liquified gas 💧 is to give the temperature at which the saturated vapour pressure is equal to atmospheric pressure - in other words the liquid's atmospheric boiling point.
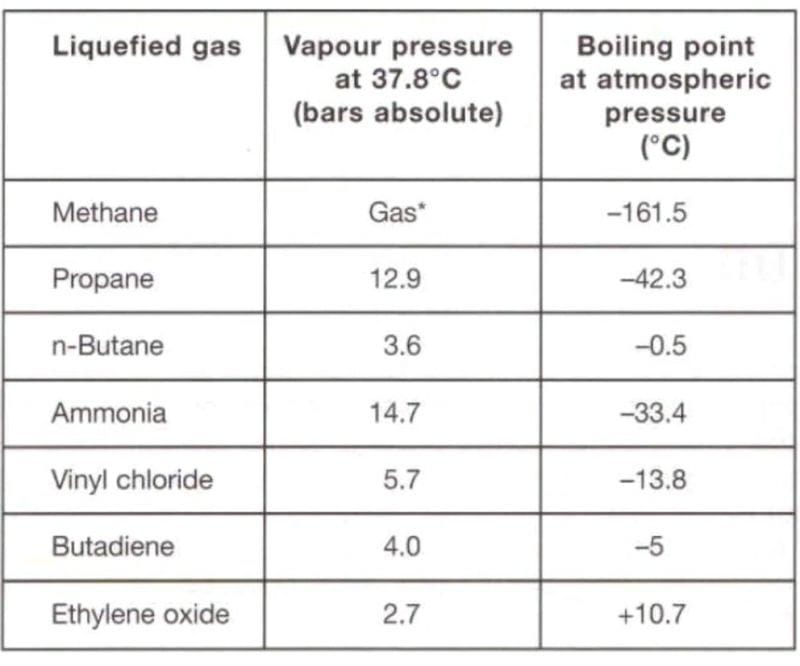
Source : McGuire&White
💰 LNGPrices
Freight rates / 174,000 m3 / 2 Stroke
Atlantic - (Spark30S) | $ 48,750 / day |
Pacific - (Spark25S) | $ 42,500 / day |
Natural Gas
Asia (JKM) - Aug 25 | $ 12.064 / mmBtu |
Europe (NWM) - Aug 25 | $ 11.014 / mmBtu |
Bunkers
$/MT | LNG | VLSFO | MGO |
Singapore | 731.32 | 543.47 | 662.00 |
Rotterdam | 705.27 | 524.11 | 674.00 |
🏭 LNGTerminals
Australia’s energy giant Woodside has completed the sale of an interest 🤝 in its liquefied natural gas (LNG) development in Calcasieu Parish, Louisiana 🏭, to Stonepeak, a New York-based investment firm specializing in infrastructure and real assets.
The U.S. player will provide 💰5.7 billion towards the expected capital expenditure for the foundation development of the project on an accelerated basis and contribute 75% of the project capital expenditure in 2025 and 2026 📅.
(C) Copyright Offshore energy 2025

Source: Woodside Energy
Cheniere Energy has taken a final investment decision (FID) on planned expansion at its Corpus Christi LNG plant and expects to grow the company’s combined production capacity to more than 60 mtpa 📈.
The US producer said it has given engineer Bechtel Energy notice to proceed with the construction of its two midscale Trains 8 and 9, which will have a combined capacity of more than 3 mtpa 💧.
(C) Copyright Tradewinds 2025

Source: Cheniere Energy
QatarEnergy has paused all channel navigation from 6pm to 5am 🚨 for tankers and gas carriers in the approaches to the major export hub of Mesaieed 📌.
This is because of safety concerns that have arisen from widespread jamming of GPS signals in the region 🛰.
(C) Copyright Tradewinds 2025

Source: Qatar Energy
Coastal Bend LNG has unveiled plans to build a 22.5-mpta LNG production and export facility on the Texas coast 🏭.
The plant will comprise up to five 5️⃣ liquefaction trains of 4.5 mtpa each.
It will also have provision for cogeneration, LNG storage tanks, and export facilities for shipping, bunkering and ISO containers 💧.
(C) Copyright Tradewinds 2025
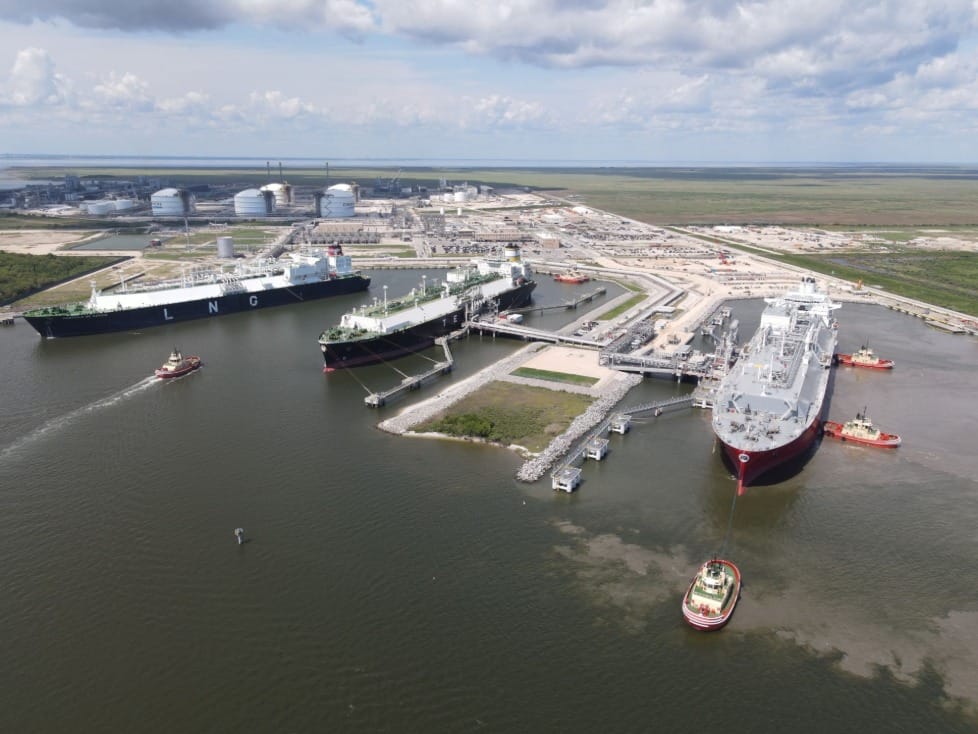

Source: Cheniere
LNG Canada has successfully loaded a first cargo of liquefied natural gas 🥇 that is now destined for global markets, marking the start of operations at Canada’s first large-scale LNG export facility 🌏.
The new LNG Canada export facility is located in Kitimat, British Columbia 🏗, in the traditional territory of the Haisla Nation. It is a long-life asset that will initially export LNG from two processing units or “trains” with a total capacity of 14 million tonnes per annum (mtpa) 💧.
The 174,000 m3 TFDE GasLog Glasgow (Built 2016) lifted this first cargo and heading now to Incheon South Korea, ETA 20th July 2025 📌.

Source: LNG Canada
🚢 LNGShips
Sanctioned LNG carrier Iris (ex-North Sky) passed through the Kara Gate entering Russia’s Northern Sea Route on June 24, likely heading for the Arctic LNG 2 plant 🏭. The move comes after the vessel spent months in ballast idling in the Barents Sea 📌.
For much of the past nine months a dozen sanctioned LNG carriers have remained largely idle 📉 and scattered across the Barents Sea on the European side and the Sea of Japan in the Far East, waiting for Arctic sea ice to recede.
(C) Copyright GCaptain 2025

Source: Shipatlas
🏗 LNGShipbuilding
The first Russian-built ice-class tanker for liquefied natural gas 🥇 is expected to go into operation in the second half of this year at the Arctic LNG 2 plant 🏭.
The tanker, named Alexey Kosygin after a Soviet statesman, was built at the Zvezda shipyard 🏗.
The tanker, already under U.S. sanctions 🚨, started sea trials at the end of last year and the final trial stage is due to begin at the end of this month.
(C) Copyright Marine Link 2025
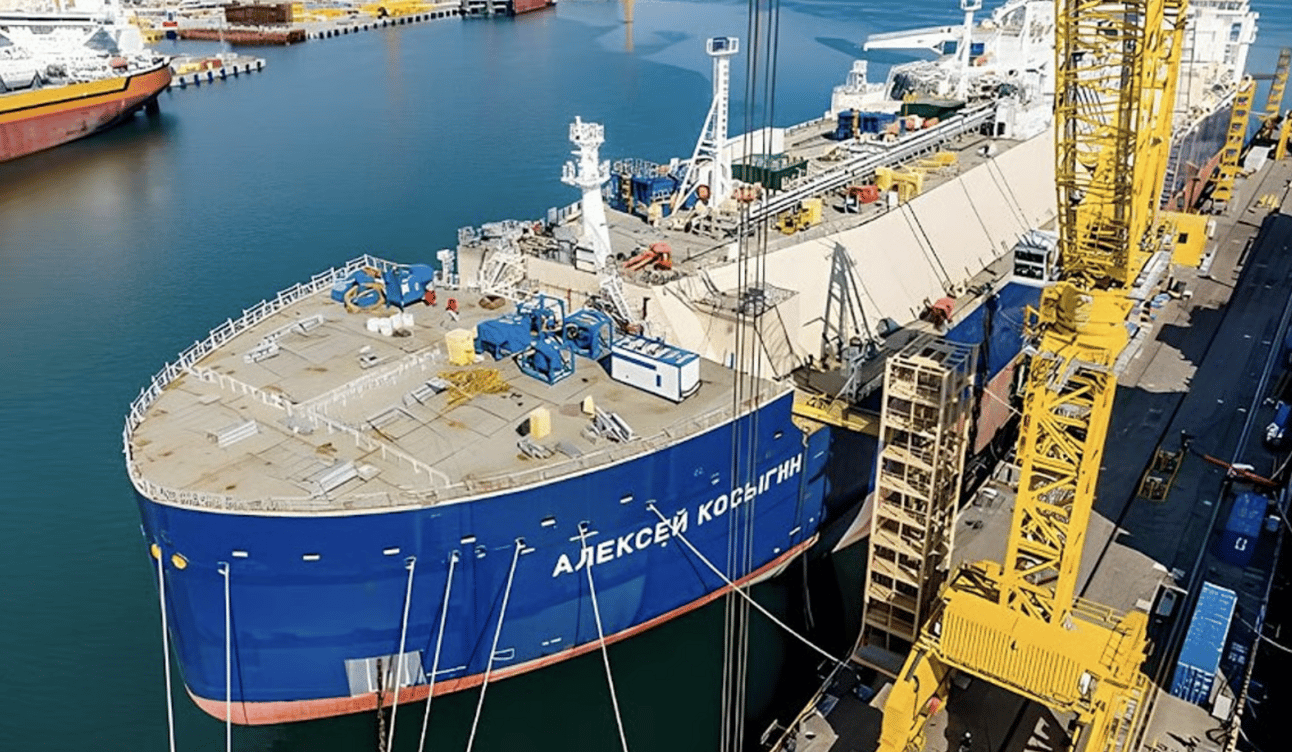

Source: Zvezda shipyard
Knutsen LNG France has taken over a liquefied natural gas (LNG) carrier from South Korea’s HD Hyundai to deliver it to its new charterer, QatarEnergy 🎊.
The 174,000-cubic-meter LNG carrier Mraikh was delivered on June 26, 2025. Nine more vessels will join it in due time 🎯.
Mraikh, which brings Knutsen’s French fleet to 👉 15 units, is equipped with the latest energy efficiency measures, including an air lubrication system and LNG-compatible boilers 🏭.
(C) Copyright Offshore Energy 2025

Source: Knutsen LNG France
Capital Group boosts LNG orderbook with 💰1bn deal at HD Hyundai Samho 🏗
Capital Group has been revealed as the shipowner behind an order for four 4️⃣ LNG carriers booked at HD Hyundai Samho.
(C) Copyright Tradewinds 2025

Source: Capital Gas
Knutsen Group has held a naming ceremony for the last in a series of LNG carrier (LNGC) newbuildings built for charterer Shell 🎊.
LNG carrier Zoe Knutsen is the ninth 9️⃣ and final vessel of a series built for Shell.
The XDF 174.000CBM Zoe Knutsen is scheduled for delivery in September 2025 🎊 and will go straight into service under charter with Shell Singapore 2025-2032, operating as part of their global LNG fleet.
(C) Copyright Riviera Maritime Media 2025
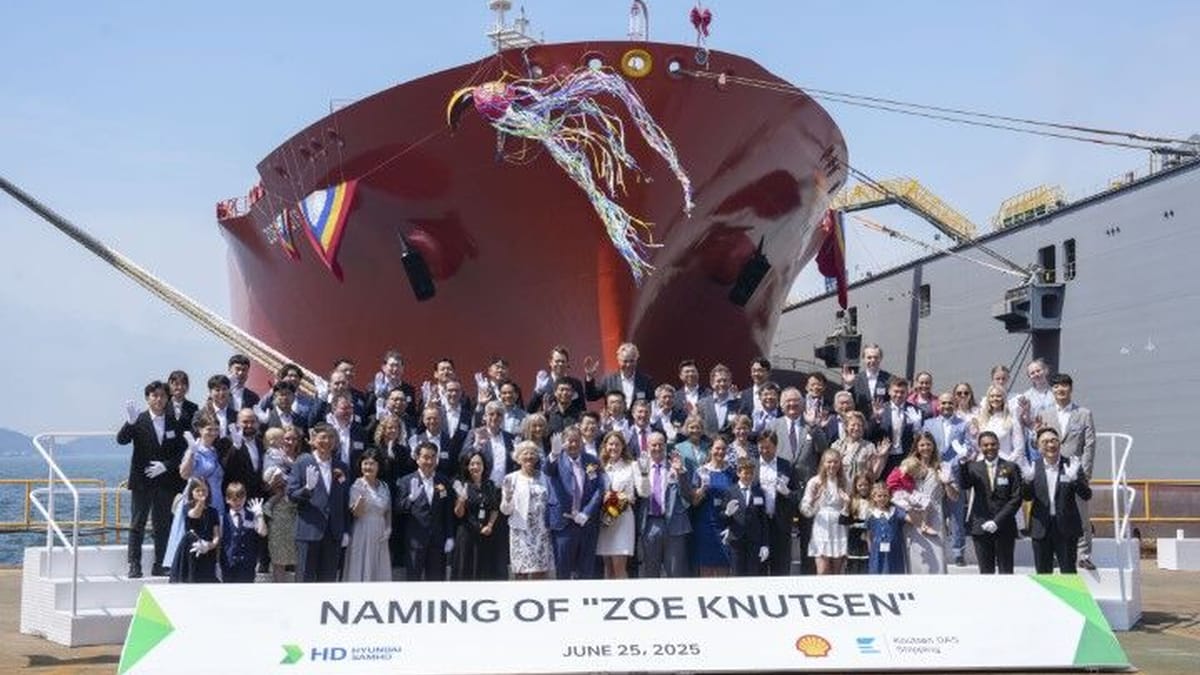

Source: Knutsen Group
🤝 LNGContracts
Chevron has taken steps to secure additional liquefied natural gas (LNG) by inking one more sale and purchase agreement (SPA) with 🤝 Energy Transfer LNG for the delivery of supplies from an LNG export project being developed on Louisiana’s Gulf Coast 🏭.
Thanks to this 20-year LNG supply agreement 📅, Chevron has increased its total commitment by 1 million tonnes per annum (mtpa) 💧 from the Lake Charles LNG export facility, enabling its total contracted volume with Energy Transfer LNG to reach 3 mtpa 💧, following the initial 2 mtpa agreement signed in December 2024.
(C) Copyright Offshore Energy 2025

Source: Energy Transfer
Thailand’s state-owned oil and gas company PTT has signed a heads of agreement (HoA) with the U.K.-based energy company Centrica Energy 🤝 for a multi-year supply of liquefied natural gas (LNG) 💧.
Under the deal, PTT is slated to deliver LNG to Centrica for ten 🔟 years on a delivered ex-ship basis across a range of destinations in Asia. Deliveries are expected to start in 2028 📅.
(C) Copyright Offshore Energy 2025

Source: PTT
💧 LNGBunkering
Gaztransport & Technigaz (GTT) and China’s Hudong-Zhonghua Shipbuilding have initiated a joint innovation project 🤝 to optimize the design and performance of LNG bunkering vessels 💧.
The partners intend to increase the effective pressure in LNG tanks to 1 bar gauge (barg) 📈 from the current industry standard of 0.7 barg using GTT’s Mark III Flex membrane containment system and leveraging previous approvals from class societies for this pressure 🎯.
GTT stated that this partnership will also evaluate the technical feasibility of increasing the design pressure to 2 barg 📈.
(C) Copyright Offshore Energy 2025

Source: GTT
Japanese shipping company Kawasaki Kisen Kaisha (K Line) has begun using bio-LNG to power its vessels 🔥 as part of a wider strategy to embrace renewable fuels and achieve net-zero greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by 2050 🌎.
The company announced the first use of bio-LNG fuel 💧supplied by Shell Western LNG, part of energy giant Royal Dutch Shell, to the car carrier Oceanus Highway.
The vessel received 500 tons of bio-LNG 💧from Shell at the Belgian Port of Zeebrugge 📌.
(C) Copyright Offshore Energy 2025

Source: GTT
🔥 LNGAsFuel
Australia’s ferry services provider TT-Line Company has welcomed the second and final LNG-powered car and passenger (RoPax) ferry built by Finland’s Rauma Marine Constructions (RMC), Spirit of Tasmania V 🎊
The ferry is equipped with four Wärtsilä 46DF dual-fuel main engines 🏭, three Wärtsilä 20DF dual-fuel auxiliary engines🏭, and two Wärtsilä LNGPac fuel storage, supply, and control systems 💧.
(C) Copyright Offshore Energy 2025

Source: RMC
⚡ AlternativeFuels
WinGD has been tapped to supply its X-DF-M dual-fuel methanol and methanol-ready X-engine designs 🏭 for over 30 boxships to be constructed for a Taiwanese container shipping player 🚢.
The methanol-ready X-92 engines are to be fitted onto vessels with a 👉 16,000 TEU capacity. The order reportedly follows a booking from earlier this year that entailed the equipping of 👉 fourteen 8,700 TEU container vessels with the X-82 solution and of 👉 six units of the same capacity with the X-82-DF-M methanol-fueled engines.
(C) Copyright Offshore Energy 2025

Source : Splash247
Stena Futura, the first methanol-ready NewMax hybrid ship built for Swedish ferry company Stena Line 🥇, has completed its sea trials in China.
Once operational, Stena Futura and sister ship Stena Connecta are expected to enhance freight capacity by 40% on the Belfast-Heysham route 📈.
Scheduled for delivery in late 2025, Stena Connecta will be equipped with Norsepower rotor sails 🌪, a wind propulsion solution from Finnish cleantech company Norsepower. Stena Futura will also be delivered as “rotor sail ready”,
(C) Copyright Offshore Energy 2025

Source : Stena Line
👨💻 LNGJobs
Shell Ship Management is looking for LNG experienced officers :
Chief Officer
Second Officer
Third Officer
2nd Engineer
3rd Engineer
4th Engineer
Electrical Engineer
Have a great week ahead !
Mustapha 👋🏻
Read Next
Did You like this LNG4U Edition ?
If YES, please share it with your friends in Social Media to grow our LNGiers community
📺 LNGAds
Want to advertise in LNG4U? → Send your request to [email protected] 🤝


